The 6 Governance Strategies to Optimize Citizen Development
In modern times, it is no longer business as usual and businesses must innovate and embrace digital transformation to survive. Off-the-shelf software will not be enough and businesses need more app development, process automation and workflow management than ever before. There is a global shortage of software developers, so how will businesses cope?
Citizen development is the answer, by empowering tech-savvy business users to build apps and innovate. Some statistics to illustrate the problem:
What is Citizen Development?
Gartner defines a citizen developer as “a user who creates new business applications for consumption by others using development and runtime environments sanctioned by corporate IT”.
Citizen development is not a new phenomenon, and in the past it was common for rogue citizen developers to bypass IT to develop custom solutions using software (like Microsoft Access or Excel) or subscribe to unsanctioned services. Notoriously known as shadow IT, these ad-hoc apps are difficult to manage and scale, often causing problems in compliance, security, quality and hidden costs among others.
So how do businesses optimize citizen development to maximize benefit? Rather than trying to restrict citizen development, businesses can adopt the following strategies to govern and maximize the value of citizen developers. With a proper governance strategy, citizen development is a win-win situation where business users can easily build apps to solve their problems while IT has visibility and oversight.
Start by formulating a Citizen Developer Governance strategy for the business as a whole. Each organization is unique, but a good guide to start is by identifying and addressing the 6Ws principle of Why, Who, What, When, Where and How.
- Reduce bottleneck on IT resources and speed up app delivery by engaging business experts directly
- Eliminate paperwork and automate error-prone manual processes
- Centralize data to avoid data silos and redundancies
Once you have the objectives, identify the users who are suitable for citizen development. The key goal with citizen development is that anyone can start developing business solutions regardless of technical background. Instead of just relying solely on professional developers, business users and non-developer IT staff are empowered to solve pressing business problems. Typically, citizen developers are:
Tech-savvy business users
Power users of existing business applications
Non-coder IT personnel
3. What: Identify Business Problems, Use Cases and Business Units
What business problems are to be solved, and what types of apps should the citizen developers build? Here, depending on the maturity of the organization and the capability of the citizen developers, you should identify the business problems and use cases that are to be addressed.
Start with non-critical departmental or business unit apps
Start with simple, less complex data or workflow apps that require little integration
Progressively expand into more important problems as expertise and experience grows.
A simple filter to identify the best targets is to look for the ones that have simple to medium complexity, but have a higher business impact i.e. apps that can directly have a positive impact on revenues or cost reduction within your enterprise.
4. When: Manage Citizen Developer Contribution and Partner with Professional Developers
It is impractical to expect citizen developers to be able to handle more complex business app requirements. Thus, it is important to determine when citizen developers are suitable, and allow them to partner with IT and professional developers when required.
Form cross-functional, multidisciplinary fusion teams consisting of members from both business and IT.
There will be limits to what pure no-code applications can achieve, so establish key roles and procedures for them to work with IT and professional developers for more critical apps, and complex ones requiring integration.
Ensure that the application platform can empower citizen developers with no-code, yet have the flexibility to allow professional developers to extend and integrate apps with code where required.
Establish a Citizen Developer Center of Excellence (COE) where all activity can be monitored and managed. The COE can maintain policies and guidelines, establish best practices, provide resources, organize onboarding and training, report to stakeholders, etc.
Where will apps be deployed, where will citizen developers be operating, and how will IT help to manage and monitor them?
- Select tools and platforms that allow apps to be easily deployed and managed, and can be monitored from a centralized location.
- The tool or platform should allow proactive monitoring of critical enterprise requirements especially in security, performance and quality.
- Delegate apps to different citizen developer teams, and distribute apps to different environments, for example group apps by use case or business units.
Business and IT should jointly decide on a common, standard set of no-code/low-code tools or platforms to be used. There is no silver bullet, and there is no single tool or platform that can meet all needs, so every organization should assess their needs and find the best fitting solutions. Some criteria that should be evaluated:
- The tools or platforms should be simple enough to be used by citizen developers, while providing the flexibility to be extended by IT and professional developers when the need arises.
- The tools or platforms do not exist in isolation, so it would be wise to choose those that fit in the organization’s existing IT infrastructure and environment.
- Establish best practices for application development e.g. consolidating data stores to ensure data consistency, standardizing naming conventions, integration and testing standards, etc.
- Training will be fundamental, so determine a path to onboard and track learning for citizen developers (and professional developers as well).
 |
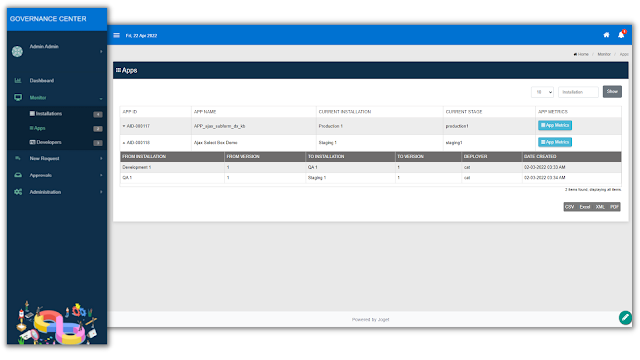
Joget DX 8 provides automated governance health checks and alerts to aid compliance in critical enterprise areas such as security, performance and application quality.
It is important to note that every organization is different and one size does not fit all. In this regard, the Governance Center itself is a Joget app so it can be tailored to an organization’s individual requirements.
Joget combines the best of business process automation, workflow management and rapid application development in a unique combination of simplicity, flexibility and openness that caters to all developer personas.
The Joget platform offers a visual no-code application development experience for citizen developers. With Joget, it is possible to visually build a complete app in minutes without coding, as described in the article 5 Minute Challenge: Go From Zero to Complete Enterprise App. There is also a more advanced example of a more complex app, with a real-time video demo showing a complete visitor management app built in less than 20 minutes.
While Joget is simple enough for users to get started on their own, organizations can initiate a formal training program to ensure that citizen developers build up sufficient skills and competencies using the Joget Academy, which provides guided learning courses and certifications.
2. Joget is Flexible and Supports a Multitude of Application Requirements
One of the key principles of the Joget platform is its openness and commitment to open standards. Not only is the core platform open source and publicly available on GitHub, Joget also offers fully flexible and scalable deployment options, whether on-premise or multi-cloud deployment (On-Demand Cloud, Certified OpenShift Operator, Red Hat Marketplace, Docker, Kubernetes, Cloud Foundry, Google Workspace Marketplace, AWS Marketplace, Azure Marketplace, GCP Marketplace).
It also runs on a multitude of operating systems, databases and application servers so it fits in with any infrastructure e.g. Windows, Linux, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, IBM Websphere, Oracle Weblogic, Red Hat JBoss EAP, Apache Tomcat, etc.
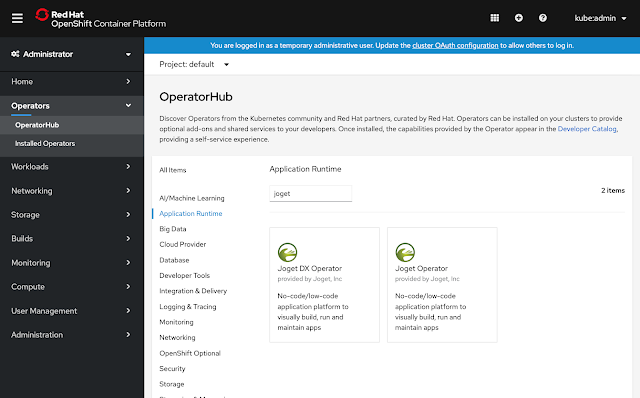
For larger scale deployments organizations can utilize the multi-tenant Joget Cloud Edition, or leverage modern cloud native computing by deploying Joget on Kubernetes or Red Hat OpenShift. With the latter, a Red Hat certified operator provides a trusted, secure and automated method to easily deploy and scale apps on a leading enterprise-grade Kubernetes platform.
Get Started with Joget DX
Joget DX 8 is now available as a limited preview to selected customers and partners, request for access today.
- Joget Demo - Experience the Joget DX platform and witness how a POC can easily be built in no time.
- Joget DX Video Tutorials - Quick overview and build your first app.
- Joget DX Knowledge Base - User and developer reference, samples and other documentation.
- Community Q&A - Ask questions, get answers, and help others.
- Language Translations - Translations for more than 20 languages.
- Joget Mindshare™ Series - Information sharing and educational content ranging from whitepapers, webinars, video tutorials, customer success stories and more.
- Joget Academy - Self-paced online learning and certification.
- Joget Marketplace - Download ready made apps, plugins, templates and more.
- Joget Events - Upcoming and past Joget events & webinars.
- Joget Press - Joget press releases.
- Joget Reviews - Joget reviews and customer testimonials.














.png)
Comments
Post a Comment